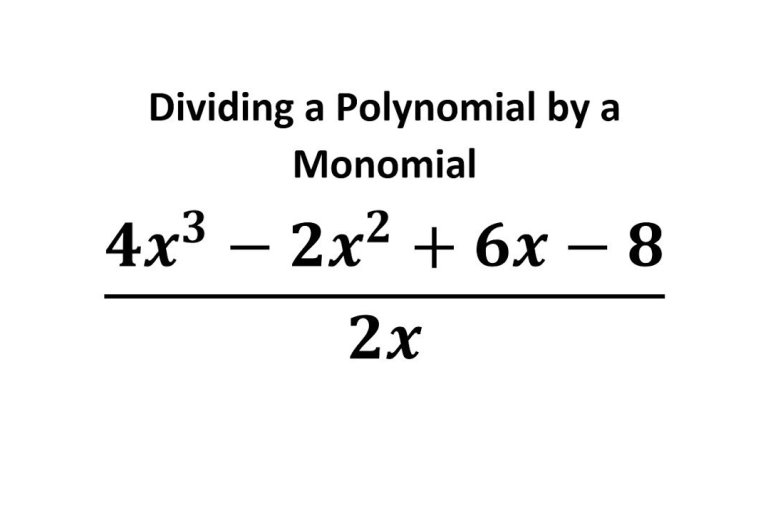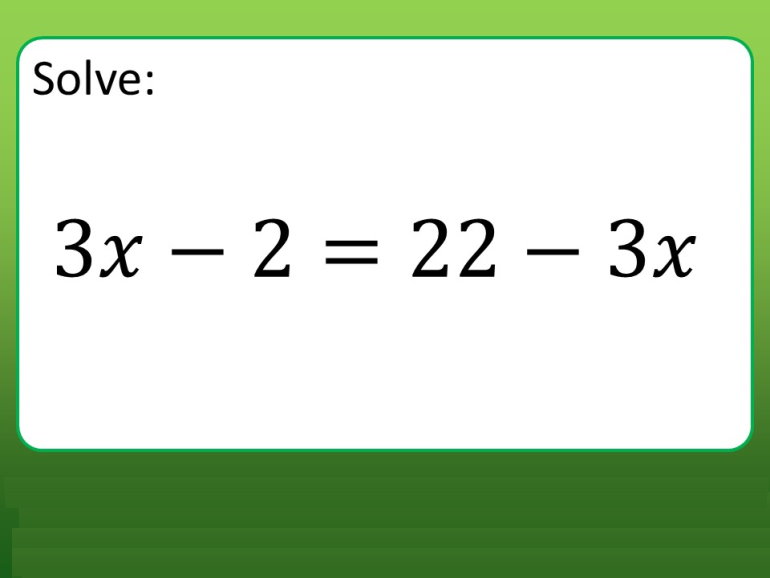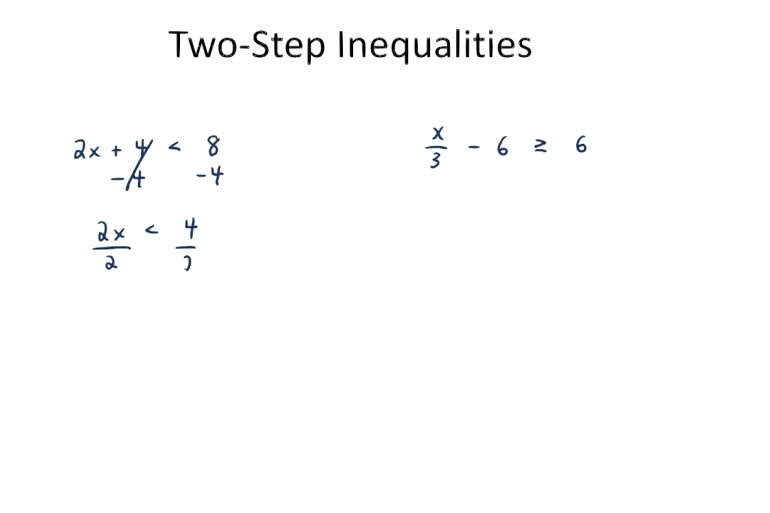1.1 Line Symmetry
After this section, you will be able to:
-
classify 2-D shapes or designs according to the number of lines of symmetry
-
identify the line(s) of symmetry for a 2-D shape or design
-
complete a shape or design given one half of the shape and a line of symmetry
-
create a design that demonstrates line symmetry
Lessons
1.2 Rotation Symmetry and
Transformations
After this section, you will be able to:
-
tell if 2-D shapes and
designs have
rotation symmetry
-
give the order of
rotation and angle of
rotation for various
shapes
-
create designs with
rotation symmetry
-
identify the
transformations in
shapes and designs
involving line or
rotation symmetry
Lessons
1.3 Surface Area
After this section, you will be able to:
-
determine the area
of overlap in
composite 3-D
objects
-
find the surface area
for composite 3-D
objects
-
create designs with
rotation symmetry
-
solve problems
involving surface
area
Lessons
2.1 Comparing and Ordering Rational Numbers
After this section, you will be able to:
-
compare and order rational numbers
-
identify a rational
number between
two given rational
numbers
Lessons
2.2 Problem Solving with Rational Numbers in Decimal Form
After this section, you will be able to:
-
perform operations
on rational numbers
in decimal form
-
solve problems
involving rational
numbers in decimal
form
Lessons
2.3 Problem Solving with Rational Numbers in Fraction Form
After this section, you will be able to:
-
perform operations
on rational numbers
in fraction form
-
solve problems
involving rational
numbers in fraction
form
Lessons
2.4 Determining Square Roots of Rational Numbers
After this section, you will be able to:
-
determine the
square root of a
perfect square
rational number
-
determine an
approximate square
root of a non-perfect
square rational
number
Lessons
3.1 Using Exponents to Describe Numbers
After this section, you will be able to:
-
represent repeated
multiplication with
exponents
-
describe how powers
represent repeated
multiplication
Lessons
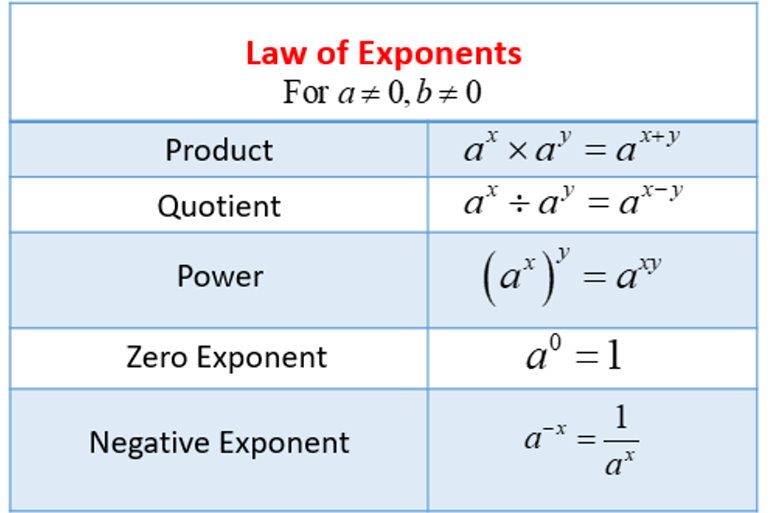
3.2 Exponent Laws
After this section, you will be able to:
-
explain the exponent
laws for
-
product of powers
-
quotient of powers
-
power of a power
-
power of a product
-
power of a quotient
Lessons
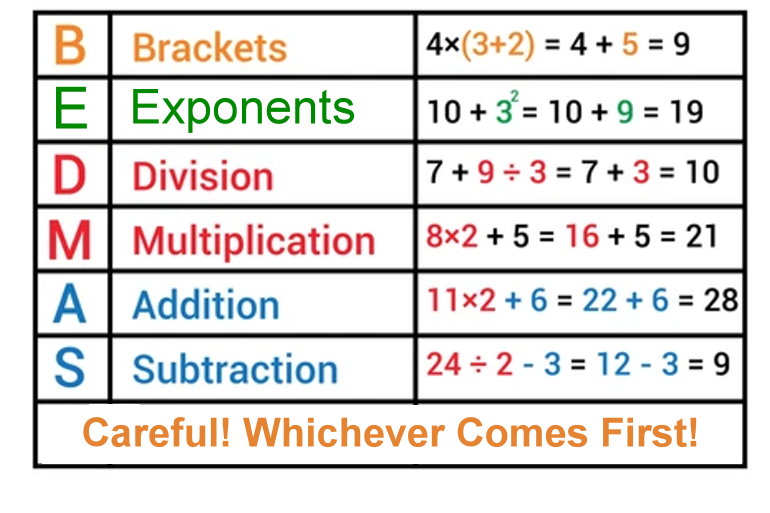
3.3 Order of Operations
After this section, you will be able to:
-
use the order of
operations on
expressions with
powers
-
apply the laws of
exponents
Lessons
3.4 Using Exponents to Solve Problems
After this section, you will be able to:
-
solve problems that
require combining
powers
-
use powers to solve
problems that
involve repeated
multiplication
Lessons
4.1 Enlargements and Reductions
After this section, you will be able to:
-
identify
enlargements and
reductions, and
interpret the scale
factor
-
draw enlargements
and reductions to
scale
Lessons
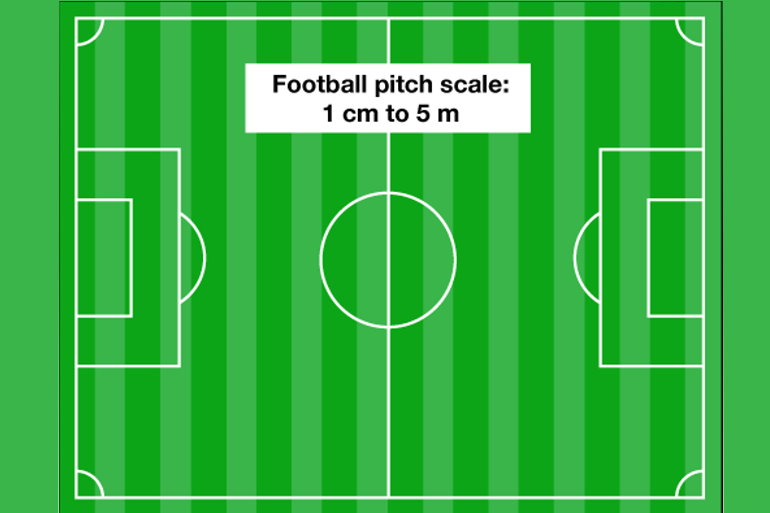
4.2 Scale Diagrams
After this section, you will be able to:
-
identify scale
diagrams and
interpret the scale
factor
-
determine the scale
factor for scale
diagrams
-
determine if a given
diagram is
proportional to
the original shape
Lessons
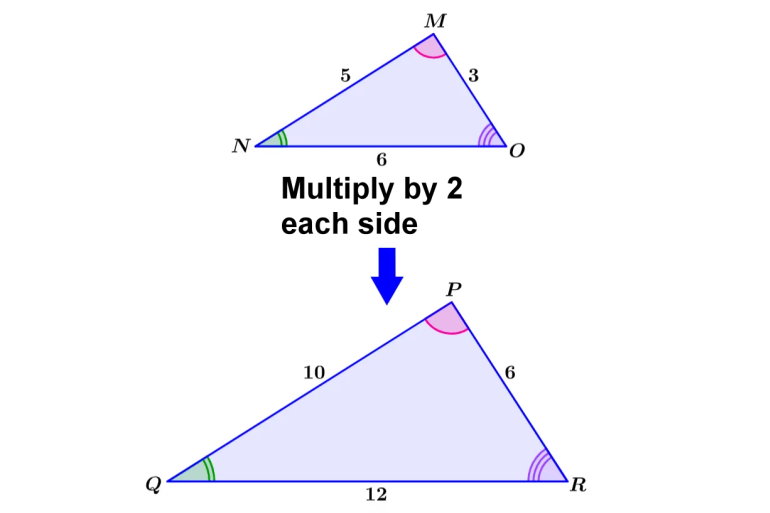
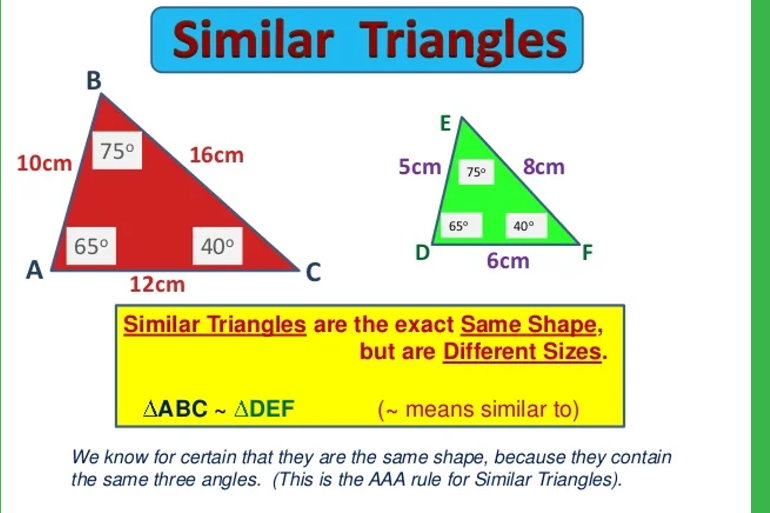
4.3 Similar Triangles
After this section, you will be able to:
-
determine similar
triangles
-
determine if
diagrams are
proportional
-
solve problems using
the properties of
similar triangles
Lessons
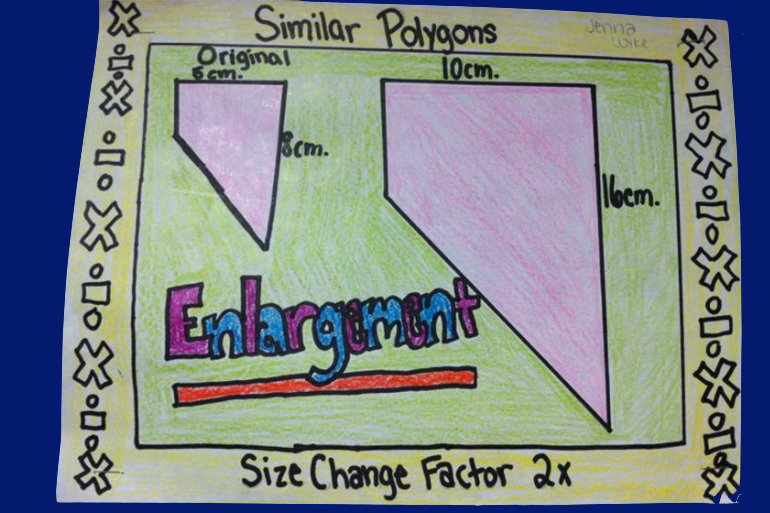
4.4 Similar Polygons
After this section, you will be able to:
-
identify similar
polygons and
explain why they are
similar
-
draw similar
polygons
-
solve problems using
the properties of
similar polygons
Lessons
5.1 The Language of Mathematics
After this section, you will be able to:
-
use mathematical
terminology to
describe polynomials
-
create a model for a
given polynomial
expression
Lessons
5.2 Equivalent Expressions
After this section, you will be able to:
-
use algebra tiles and
diagrams to show
whether expressions
are equivalent
-
identify equivalent
expressions that are
polynomials
-
combine like terms
in algebraic
expressions
Lessons
5.3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
After this section, you will be able to:
-
add polynomial
expressions
-
determine if
diagrams are
proportional
-
subtract polynomial
expressions
-
solve problems using
the addition and
subtraction of
polynomials
Lessons
6.1 Representing Patterns
After this section, you will be able to:
-
represent pictorial,
oral, and written
patterns with linear
equations
-
describe contexts
for given linear
equations
-
solve problems that
involve pictorial,
oral, and written
patterns using a
linear equation
-
verify linear
equations by
substituting values
Lessons
6.2 Interpreting Graphs
After this section, you will be able to:
-
describe patterns
found in graphs
-
extend graphs to
determine an
unknown value
-
estimate values
between known
values on a graph
-
estimate values
beyond known
values on a graph
Lessons
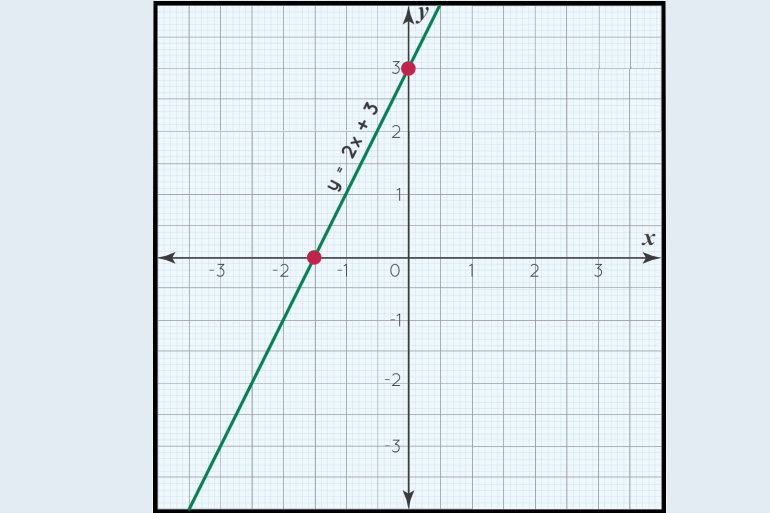
6.3 Graphing Linear Equations
After this section, you will be able to:
-
graph linear
relations
-
match equations of
linear relations with
graphs
-
solve problems by
graphing a linear
relation and
analysing the graph
Lessons
7.1 Multplying and Dividing Monomials
After this section, you will be able to:
-
multiply a monomial
by a monomial
-
divide a monomial
by a monomial
Lessons
7.2 Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials
After this section, you will be able to:
-
multiply a
polynomial by
a monomial
Lessons
7.3 Dividing Polynomials by Monomials
After this section, you will be able to:
-
divide a polynomial
by a monomial
Lessons
8.1 Solving Equations: ax=b x/a = b,a/x = b
After this section, you will be able to:
-
model problems
with linear equations
that can be solved
using multiplication
and division
-
solve linear
equations with
rational numbers
using multiplication
and division
Lessons
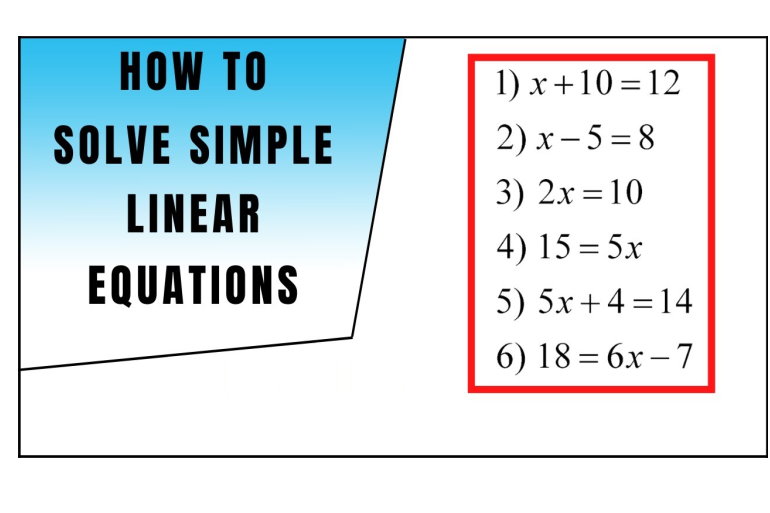
8.2 Solving Equations: ax + b = c, x/a + b = c
After this section, you will be able to:
-
model problems
with linear equations
involving two
operations
-
solve linear
equations with
rational numbers
using two operations
Lessons
8.3 Solving Equations: a(x +b) = c
After this section, you will be able to:
-
model problems
with linear equations
that include
grouping symbols on
one side
-
solve linear
equations that
include grouping
symbols on one side
Lessons
8.4 Solving Equations: ax = b + cx, ax +b = cx + d, a(bx + c) = d(ex + f)
After this section, you will be able to:
-
model problems
with linear equations
that include
variables on both
sides
-
solve linear
equations that
include variables
on both sides
Lessons
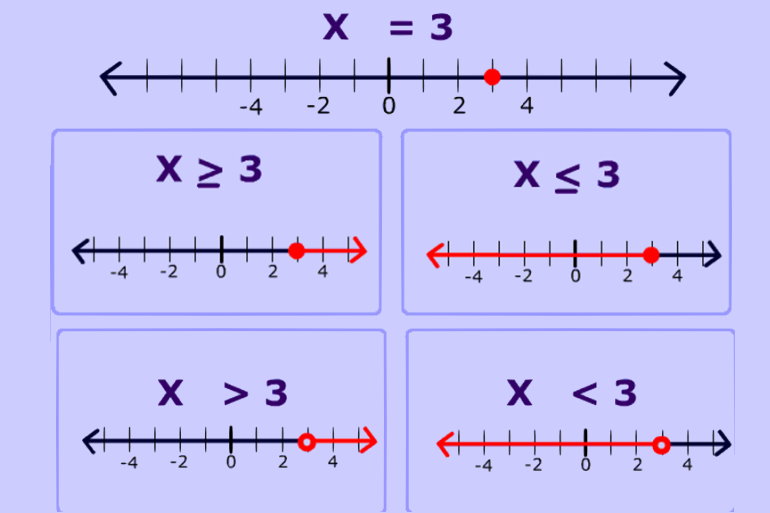
9.1 Representing Inequalities
After this section, you will be able to:
-
represent single variable linear inequalities verbally,
algebraically, and
graphically
-
determine if a given
number is a possible
solution of a linear
inequality
Lessons
9.2 Solving Single-Step Inequalities
After this section, you will be able to:
-
solve single-step
linear inequalities
and verify solutions
-
compare the
processes for solving
linear equations and
linear inequalities
-
compare the
solutions of linear
equations and linear
inequalities
-
solve problems
involving single-step
linear inequalities
Lessons
9.3 Solving Multi Step Inequalities
After this section, you will be able to:
-
solve multi-step
linear inequalities
and verify their
solutions
-
compare the
processes for solving
linear equations and
linear inequalities
-
solve problems
involving multi-step
linear inequalities
Lessons
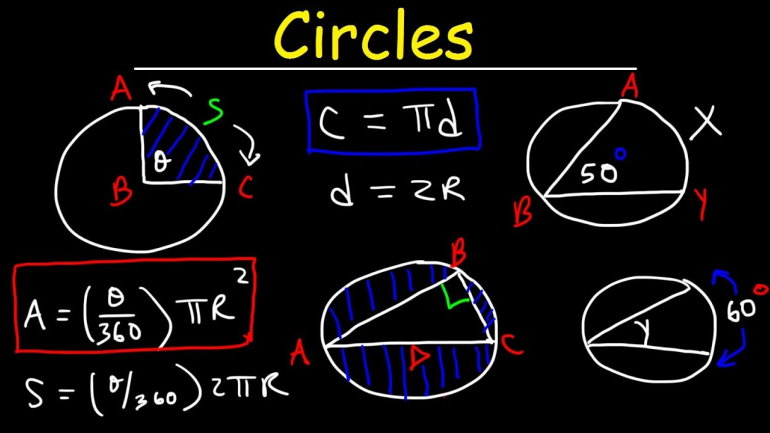
10.1 Exploring Angles in a Circle
After this section, you will be able to:
-
describe a
relationship between
inscribed angles in
a circle
-
relate the inscribed
angle and central
angle subtended by
the same arc
Lessons
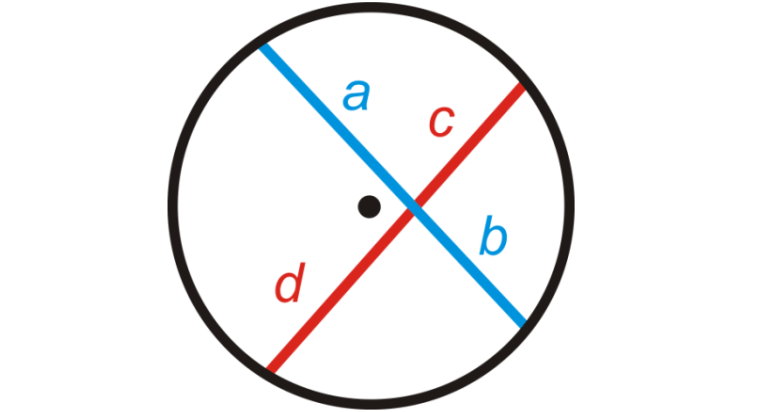
10.2 Exploring Chord Properties
After this section, you will be able to:
-
describe the
relationship among
the centre of a circle,
a chord, and the
perpendicular
bisector of the chord
Lessons
10.3 Tangents to a Circle
After this section, you will be able to:
-
relate tangent lines
to the radius of the
circle.
Lessons
11.1 Factors Affecting Data Collection
After this section, you will be able to:
-
identify how bias,
use of language,
ethics, cost, time and
timing, privacy, and
cultural sensitivity
may influence the
collection of data
-
write and analyse
appropriate survey
questions
Lessons
11.2 Collecting Data
After this section, you will be able to:
-
identify the
difference between
a population and a
sample
-
identify different
types of samples
-
justify using a
population or a
sample for given
situations
-
determine whether
results from a sample
can be applied to a
population
Lessons
11.3 Probability in Society
After this section, you will be able to:
-
identify and explain
assumptions linked
to probabilities
-
explain decisions
based on
probabilities
Lessons
11.4 Developing and Implementing a Project Plan
After this section, you will be able to:
-
develop a research
project plan
-
complete a research
project according to
a plan, draw
conclusions, and
communicate
findings
-
self-assess a research
project by applying a
rubric
Lessons